Getting Started
Core Concepts
Understand key concepts and implement our APIs using coding best practices.
Before diving into Captain Data’s API, it’s essential to understand the core concepts that define how our platform functions.
A strong grasp of these fundamentals will help you seamlessly integrate our APIs into your application.
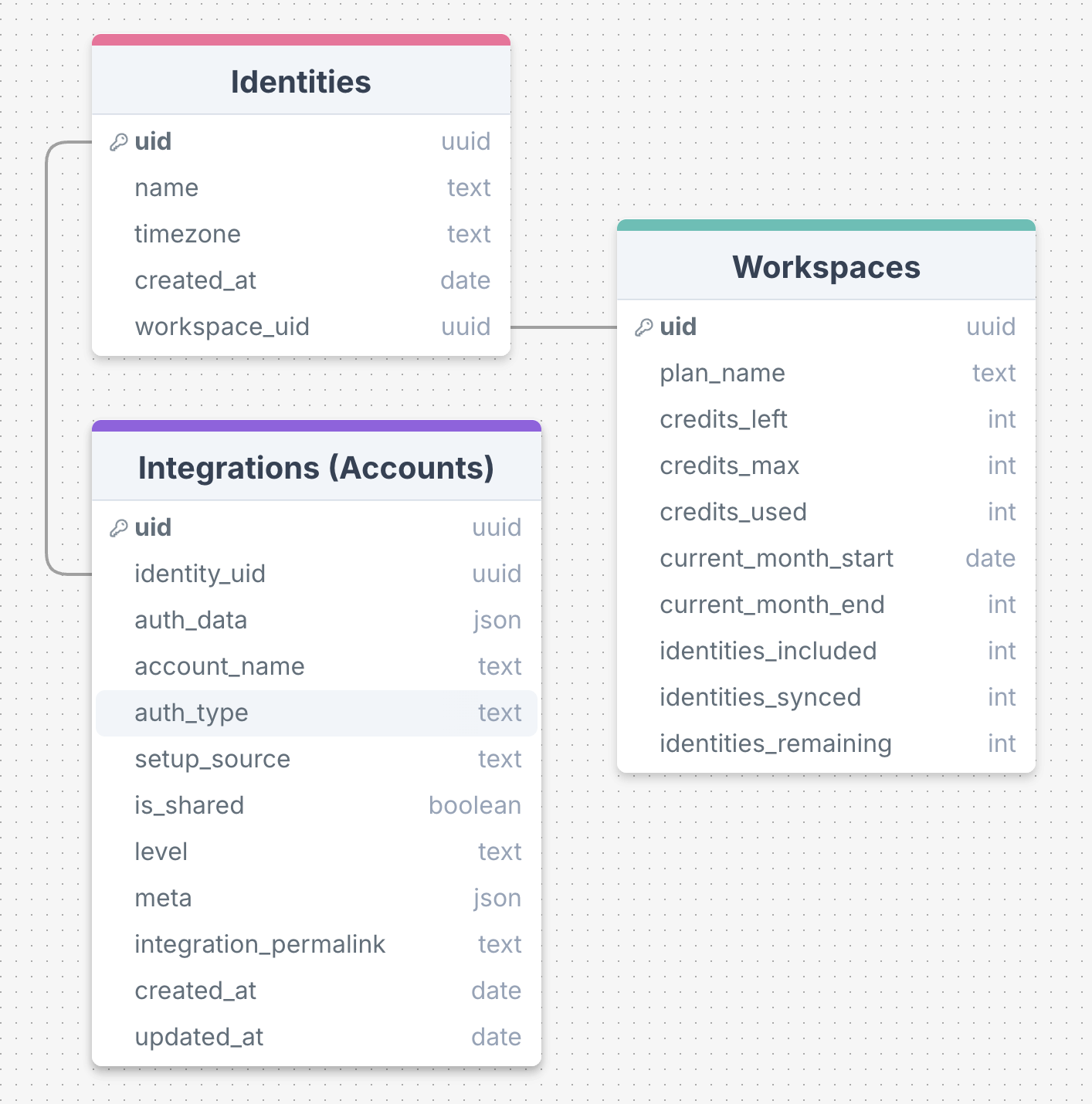 The complete Diagram is accessible here.
For detailed comparisons and use case recommendations, see LinkedIn Identities Options: Sync, Rent, or Use Managed.
For setup and implementation details, see Monitor LinkedIn Integration Status with Webhooks.
The complete Diagram is accessible here.
For detailed comparisons and use case recommendations, see LinkedIn Identities Options: Sync, Rent, or Use Managed.
For setup and implementation details, see Monitor LinkedIn Integration Status with Webhooks.
Overview of Core Entities

Relationships between core entities in Captain Data (v4) are depicted in the diagram above.
Identities vs. Workspace Members
Captain Data distinguishes between two core types of entities:- Workspace Members: These are people who have access to the Captain Data platform itself (e.g., your team, admins, or clients). They can log in, manage settings, and access the dashboard. Workspace members have roles such as Owner, User, or Ops. Workspace members are invited by the admin via the Members page.
- Identities: These represent the end users or accounts (e.g., LinkedIn profiles) that perform automated actions via the API. Identities do not have access to the platform and are used solely for automation and integration purposes.
Workspace Member Roles
- Owner: Full platform access. Can manage Members, Identities, Integrations, Billing, and Subscriptions.
- Ops: Advanced permissions, including full management of Identities and Integrations. Cannot access billing or subscription settings.
- User: Read-only access to the platform. Cannot modify settings, manage members, or access billing.
What is an Identity?
An Identity in Captain Data corresponds to an end user in your SaaS platform or AI agent platform. It is used to perform automated Actions.Identities are required to trigger actions that need to be “logged in”—for example,
sending messages or accepting invitations on behalf of a user.
For generic enrichment actions that do not require a specific account,
you can use Managed Identities
which are pre-configured accounts managed by Captain Data. Identities do not have access to the Captain Data platform
and are ideal for mapping your SaaS users (as identities) to integration accounts.
They are primarily used for linking and sharing integrations via API.
Identity Modes
Captain Data supports three identity modes to control how accounts are used for action execution:- Direct Mode: Use specific identities for precise control
- Auto Mode: Automatic distribution across all available accounts
- Managed Mode: Use Captain Data’s pre-configured account pool (1.5× credit cost)
Managed mode cost: Using
identity_mode: "managed" costs 1.5× the standard credit cost but requires no setup.Managing Identities
1
(Optional) Invite a Member
Invite a new workspace member via the platform settings if you want a person to have access to the Captain Data dashboard. Members can be team members, admins, or clients.
2
Create an Identity
Create an Identity to represent an end user or account (e.g., a LinkedIn profile) that will perform automated actions. Identities are not linked to members by default, but a member can also be an identity if needed.
3
Connect the Identity to an Integration
Either the Member connects the Identity to an integration (like LinkedIn) directly via the dashboard, or the connection is handled programmatically via the API.
- Identity licenses are included in your plan (e.g., 5 identities in the Free Trial).
- Identities can be added at no cost until you reach your plan’s license limit. Each plan includes a set number of identity seats - check captaindata.com/pricing for your plan’s allocation.
As you scale, you’ll hit fair-use thresholds where we’ll limit the number of
identities you can sync to Captain Data. Contact sales@captaindata.co to learn
more.
Securing Identities
At Captain Data, your identity security is paramount. Every identity is assigned a unique IP address to enhance security. Learn more about identity management and security here.Integrations
What is an Integration?
An Integration represents a connection to an external service, such as LinkedIn or HubSpot, that you can access through our APIs.- An Integration belongs to a single Identity.
- Integrations authenticate your requests with third-party APIs and services.
LinkedIn Specifics
- Captain Data applies smart limitations to prevent LinkedIn integration restrictions.
- Supported LinkedIn licenses include Sales Navigator, Premium, and Recruiter Lite.
- Renting LinkedIn integrations is available to help you avoid the hassle of managing or warming up connections.
- Smart Limitations for LinkedIn Integrations
- Supported LinkedIn Licenses
- LinkedIn Identities Options: Sync, Rent, or Use Managed
LinkedIn Integration Webhooks
LinkedIn Integration Webhooks provide real-time notifications for LinkedIn account status changes, allowing you to monitor integration health and react to authentication issues. Key Features:- Real-time status notifications
- Event types:
AUTH_SUCCESS,AUTH_PENDING,AUTH_FAILED,AUTH_EXPIRED - Automatic monitoring of integration health
- Proactive handling of authentication issues
Webhooks are essential for maintaining reliable LinkedIn integrations and ensuring your automation continues running smoothly.
Real-time API Access
What is the API?
Our v4 API provides direct, real-time access to data from various sources.- No more waiting for jobs or workflows to complete
- Instant results through RESTful endpoints
- Standardized error handling and response formats
API Features
-
Real-time Responses:
- Get data immediately when you make a request
- No need to poll or wait for job completion
-
RESTful Design:
- Standard HTTP methods (GET, POST, etc.)
- Clear endpoint structure
- Consistent response formats
-
Error Handling:
- Standardized error responses with the following structure:
- Error scopes include:
input,integ,param,config - Each error includes a unique reference ID for tracking
- Additional parameters may be included in the
paramsobject - Rate limiting information is provided in headers
- Standardized error responses with the following structure:
Async API Mode
What is Async Mode?
Async mode provides an alternative way to process large volumes of data or long-running operations.- Submit requests for background processing
- Receive a run ID to track progress
- Use callbacks for completion notifications
- Manage callback history and retry failed callbacks
- Ideal for batch operations or when real-time responses aren’t required
When to Use Async Mode
-
Large Data Sets:
- Processing thousands of records
- Complex data transformations
- Bulk operations
-
Long-running Operations:
- Operations that take more than 30 seconds
- Resource-intensive tasks
- Rate-limited operations
-
Background Processing:
- Non-critical operations
- Scheduled tasks
- Batch processing
While async mode provides more flexibility for large-scale operations, real-time mode is recommended for most use cases due to its simplicity and immediate results.
Schedule API Mode
What is Schedule Mode?
Schedule mode provides a way to plan processes of large volumes of data or long-running operations.- Define a start date with
schedule_atand/or recurrence with acronexpression, andtimezone - Automate time-based launches of operations
- Receive a schedule ID to track progress
- Use callbacks for completion notifications at each new Run
- Manage callback history and retry failed callbacks
- Ideal for campaigns, regular updates, or off-peak executions
When to Use Schedule Mode
- Time-based Automation:
- Launch operations at a specific time
- Coordinate actions with business hours or target time zones
- Automate reminders, reports, or follow-ups
-
Recurring Jobs:
- Daily/weekly/monthly scheduling
- Periodic data syncs or reporting tasks
- Maintenance or update routines
-
Load Distribution:
- Shift workload outside of peak hours
- Optimize resource usage during low-traffic periods
- Mitigate rate limit risks through off-hours scheduling
While schedule mode enables precise timing and automation, use async or real-time modes when immediate execution is required.

